Intro to the shell
Basic shell commands
| Command | Use |
|---|---|
| pwd | Print current (working directory) |
| ls my_directory | List files in a directory |
| cd my_path | Define (go to) current directory |
| cd | Return to HOME directory |
| cd ../ | Go to parent directory |
| rm my_file | Remove file (!no way back!) |
| mkdir my_directory | Create directory |
| rmdir -rf my_directory | Remove directory (!no way back!) |
| cp path_to_source path_to_destination | Copy file or directory |
| mv path_to_source path_to_destination | Move file or directory |
Ctrl-Shift-C | Copy some text in vim editor |
Ctrl-Shift-V | Paste some text in vim editor |
| vim path_to_text_file | Open text file using vim |
| unzip path_to_archive_file -d path_to_destination | Unzip a .zip archive in a directory |
Ctrl-C | Cancel current command |
Good practices
Working on the terminal can difficult in the beginning. One difficulty is to always know where you are located in the file tree.
- Use
pwdcommand to print the current directory. -
Use
ls(list) orll(long list) commands to print the content of the current directory. Use it often… Typically after a command that create outputs, to check whether they are created…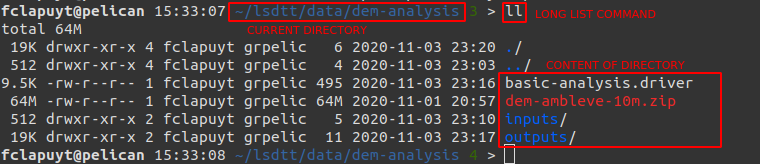
- Use
Tabkey to auto-complete file names and directory names. HitTabkey again to get a list of possibilities, if there are several ones. - Use
UpandDownarrows of the keyboard to navigate in the history of commands that you already executed.
Paths (examples on the Pelican server)
Some facts about paths to directories and files:
- When you connect to the Pelican server, you land in your
HOMEdirectory. - The absolute path of your
HOMEdirectory is:/home/elic/MY_LOGIN. - Anywhere in the file tree, execute the
cdcommand to return theHOMEdirectory. - Absolute paths are always written with respect to the
rootof the file tree, i.e./. - A typical absolute path to the DEM file would be:
/home/elic/MY_LOGIN/lsdtt/data/dem-analysis/mnt-ambleve-10m.tif. Notice the/at the beginning of the path, indicating that it is an absolute path, i.e. starting from theroot. - A typical relative path to the DEM file, if you are located in your
HOMEdirectory:lsdtt/data/dem-analysis/mnt-ambleve-10m.tif. Note that there is no/at the beginning of the path. - Relative paths are always expressed relatively to the current directory.
- To know the current directory, use the
pwdcommand (print working directory).
Sequence of example commands
Type and execute the following sequence of commands to learn how to communicate with the server:
# Print working directory
pwd
# List files in current directory
ls
# create new directory
mkdir dem-analysis
# create file in dem-analysis directory
vim dem-analysis/params.txt
# type i to activate insert mode, write something, hit Esc to quit edit mode, type ":wq" to write and quit the file
# List files in dem-analysis directory
ls dem-analysis
# Enter dem-analysis directory
cd dem-analysis
# List files in current direct
ls
# List files in parent directory
ls ../
# Create new directory in current directory
mkdir outputs
# list files in current directory
ls
# Copy params.txt into outputs directory with a new name
cp params.txt outputs/params-v2.txt
# Return to HOME directory
cd
# Enter outputs directory
cd dem-analysis/outputs
# Modify params-v2.txt file. Use "Ctrl-Shift-C" to copy and "Ctrl-Shift-V" to paste text.
vim params-v2.txt
# Print working directory
pwd
# Return to dem-analysis directory. The ~ is a way to create a path from the HOME directory. Useful when your are "lost" in the file structure.
cd ~/dem-analysis
# Copy outputs as a new directory. The "-r" parameter is for "recursive", i.e. it will copy all subdirectories too.
cp -r outputs outputs-v2
# List files in current directory
ls
# Delete outputs/params.txt
rm outputs/params-v2.txt
# Delete params.txt in current directory. The "-f" parameter is for "force".
rm -f params.txt
# Delete outputs-v2.
rm outputs-v2
# To delete non-empty directories, do not forget the "-rf" parameters
rm -rf outputs-v2
# List files in current directory
ls
# Return to HOME directory
cd
# Delete dem-analysis directory
rm -rf dem-analysis